In India, the leading cause of chronic kidney disease is diabetes. Are you well-informed about it? Read to discover what it is, the risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and more.
What is diabetic nephropathy?
Diabetic nephropathy is a long-standing complication of diabetes. As a result of chronically elevated blood sugar levels, the kidneys’ delicate filtering system gets damaged, hampering their ability to filter and remove waste products. The damage progresses slowly over the years and may eventually result in kidney failure unless it is addressed at an earlier stage.
What are the risk factors for diabetic nephropathy?
- Long-standing uncontrolled diabetes
- Uncontrolled blood pressure
- High blood cholesterol levels
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Family history of diabetes and kidney disease
What are the symptoms of diabetic nephropathy?
- Swelling of the face, hands, and feet
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Dyspnoea
- Frothy urine
- Dry and itchy skin
- Confusion
- Muscle cramps
What is the earliest sign of diabetic nephropathy?
Microalbuminuria or the presence of minute amounts of the protein albumin in the urine, is the earliest sign.
When should I consult a doctor?
You must consult a doctor if you notice swelling in your legs or feet, frothy urine, or any other symptom of diabetic nephropathy. The swelling is typically called pitting oedema because there will be pitting in the region when you firmly press it. This type of swelling occurs due to fluid retention. It is important to consult a doctor at the earliest stage, as it helps to initiate treatment at an early stage and thereby avoid severe complications.
How is diabetic nephropathy diagnosed?
- Blood test: Kidney function tests including blood urea, and serum creatinine levels (your doctor calculates the degree of kidney damage based on creatinine level)
- Urine test : To detect the level of proteins, albumin, and creatinine in the urine
- Ultrasound : To find out about the structure, size, and extent of damage to your kidneys
What is the normal creatinine level in the blood?
For men, 0.8 to 1.4 mg/dL of creatinine is considered normal. Due to their typically lower levels of muscle mass, females often have lower levels of creatinine (0.6 to 1.2 mg/dL) compared to males.
What are the stages of diabetic nephropathy?
| Stage | Glomerular Filtration Rate | Status of the kidney |
|---|---|---|
| Stage I | 90 or higher | Mild kidney damage |
| Stage II | 89-60 | Slightly more damaged; still, the kidney functions well |
| Stage III | 59-30 | Mild to severe loss of kidney function |
| Stage IV | 29-15 | Severe loss of kidney function |
| Stage V | Below 15 | Nearing or at complete kidney failure |
What is the treatment for diabetic nephropathy?
The treatment plan for diabetic nephropathy depends on the degree of damage and the stage of kidney disease at the time of diagnosis.
In the early stages, management involves regulating your blood sugar levels. This means your medicines may be changed, you may be advised certain diet restrictions to decrease the salt intake, and restrictions on daily fluid intake. You may be prescribed medicines that are protective for your kidneys.
In advanced stages, you may have to undergo dialysis and a kidney transplant to enhance your quality of life.
Can diabetes nephropathy be reversed?
No, kidney damage that has already occurred can not be reversed. However, you can slow down or arrest the progression of damage and protect your kidneys from further impairment by following a strict diet, taking your medicines regularly, and being physically active.
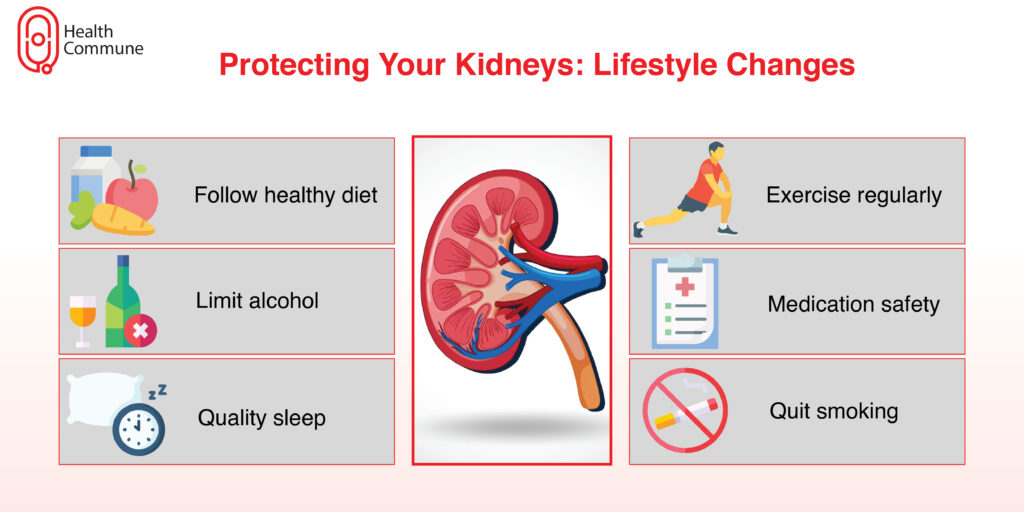
I have diabetic nephropathy. How do I change my lifestyle to protect my kidneys from further damage?
- Follow a healthy diet. Minimising your salt intake and following special diets such as the DASH diet and Mediterranean diet may be helpful. Additionally, you can be asked to monitor and limit your fluid intake
- Exercise regularly
- Avoid over-the-counter painkillers. Consult your doctor before taking medicines since some of them can further aggravate kidney damage
- Quit smoking
- Limit your alcohol intake
- Ensure that you sleep properly
What are the complications of diabetic nephropathy?
- Fluid retention
- Increase in potassium levels in the blood
- Anaemia
- Damage to the heart and blood vessels
- Bone disorders and mineral imbalance
How can I prevent diabetic nephropathy?
- Ensure that your blood sugar levels are well regulated
- Manage high blood pressure
- Avail treatment for high blood cholesterol
- Eat a healthy and nutritious diet
- Ensure that you exercise routinely
- Regularly monitor your blood parameters and frequently follow up with your doctor



