What is hyperthyroidism?
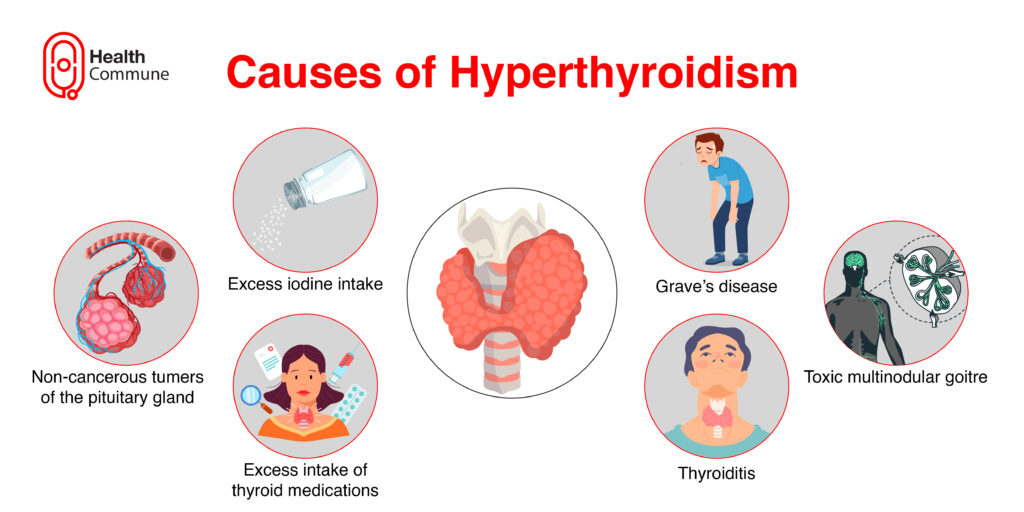
What are the causes of hyperthyroidism?
Causes include :
- Graves disease (an autoimmune condition where the body produces antibodies that stimulate your thyroid gland, thereby producing more thyroid hormones)
- Toxic multinodular goiter (growth of nodules on the thyroid, gland which can produce thyroid hormones)
- Non-cancerous tumours of the thyroid gland
- Inappropriate and excessive use of medicines prescribed for hypothyroidism (synthetic thyroxine or levothyroxine)
- Thyroid hormone-secreting cells in some other parts of the body (for example, the ovaries)
- Thyroiditis, or inflammation of the thyroid gland (in some cases, thyroiditis causes leakage of thyroid hormones into the bloodstream, resulting in symptoms of hyperthyroidism)
- Medicines such as amiodarone and other iodine-containing drugs
What are the risk factors for hyperthyroidism?
Risk factors for hyperthyroidism include :
- Family history of thyroid disease
- Certain medical, conditions like type 1 diabetes
- Excess iodine intake in food
What are the symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
Symptoms include :
- Weight loss
- Increased appetite
- Abnormally rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
- Nervousness
- Shaking
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Diarrhoea
- Muscle weakness
- increased sensitivity to heat
- Abnormally increased sweating
- Changes in the menstrual cycle
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland
- Increased body temperature
What is the difference between goiter and hyperthyroidism?
How is hyperthyroidism diagnosed?
If you present symptoms of hyperthyroidism to your doctor, they may prescribe certain blood tests to evaluate the level of thyroid hormones in your body. These blood tests include :
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
- T4
- Free T3 and T4
- In addition to these, you may also be advised to undergo :
- Ultrasound scan
- Radioactive iodine uptake test (The thyroid gland uses iodine to produce thyroid hormone. An overactive thyroid gland would take up and retain more iodine)
- Thyroid receptor antibody testing
- Radioisotope scan of the thyroid gland
How is hyperthyroidism treated?
The treatment of hyperthyroidism is determined based on the cause and severity. The different treatment options available are :
- Medicines that minimise thyroid function (antithyroid medicines, beta-blockers)
- Surgery
- Radioactive iodine
Are there any side effects to hyperthyroidism treatment?
Surgery and radioactive iodine stop the thyroid gland from producing excess thyroxine, but, as a side effect, they may make the thyroid gland underactive. Hence, you may have to take synthetic thyroid hormones to supplement the decreased level of thyroid hormones.
Anti-thyroid medications can cause minor side effects, such as allergic reactions. These medicines can cause a severe drop in white blood cells (called agranulocytosis) and liver damage in some people.
Is hyperthyroidism curable?
How will hyperthyroidism impact my pregnancy?
Mild hyperthyroidism during pregnancy is usually unproblematic. However, uncontrolled hyperthyroidism can lead to complications such as premature birth and low birth weight for your baby. There is also an increased risk of pregnancy-induced high blood pressure in women with hyperthyroidism.
What are the complications of hyperthyroidism?
Some of the complications of hyperthyroidism are :
- Heart failure
- Stroke
- Osteoporosis (loss of the mineral structure of bone. this condition is associated with an elevated risk of fractures)
- Eye problems: bulging, red, and swollen eyes, along with vision problems
- Thyrotoxic crisis: sudden intensification of the symptoms of hyperthyroidism leading to fever, profuse sweating, increased pulse rate, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhoea. This can be triggered by the sudden discontinuation of anti-thyroid medicines, illnesses (such as an infection), or surgery. If emergency medical care is not provided, this condition can be life-threatening.
What lifestyle modifications can help me manage hyperthyroidism?
- A healthy, protein-rich diet
- Exercises (mood-lifting, cardiovascular exercises, strength training to prevent osteoporosis)
- Stress management and relaxation techniques




